- try-catch, throw Exception2024년 07월 24일
- chantleman
- 작성자
- 2024.07.24.:06
프로그램을 실행했을 때 에러가 니는 경우
예외처리를 하지 않았으면 프로그램이 바로 종료됩니다.
하지만 실제 우리가 프로젝트를 만들때 프로그램이 종료되면 안되기때문에
에러발생해도 프로그램 종료되지 않도록 예외처리를 꼭 해줘야 합니다.
System.out.println("숫자입력: "); int num = sc.nextInt();그냥 이렇게만 하면 숫자 대신 문자입력했을 때 InputMismatchException 에러가 납니다.
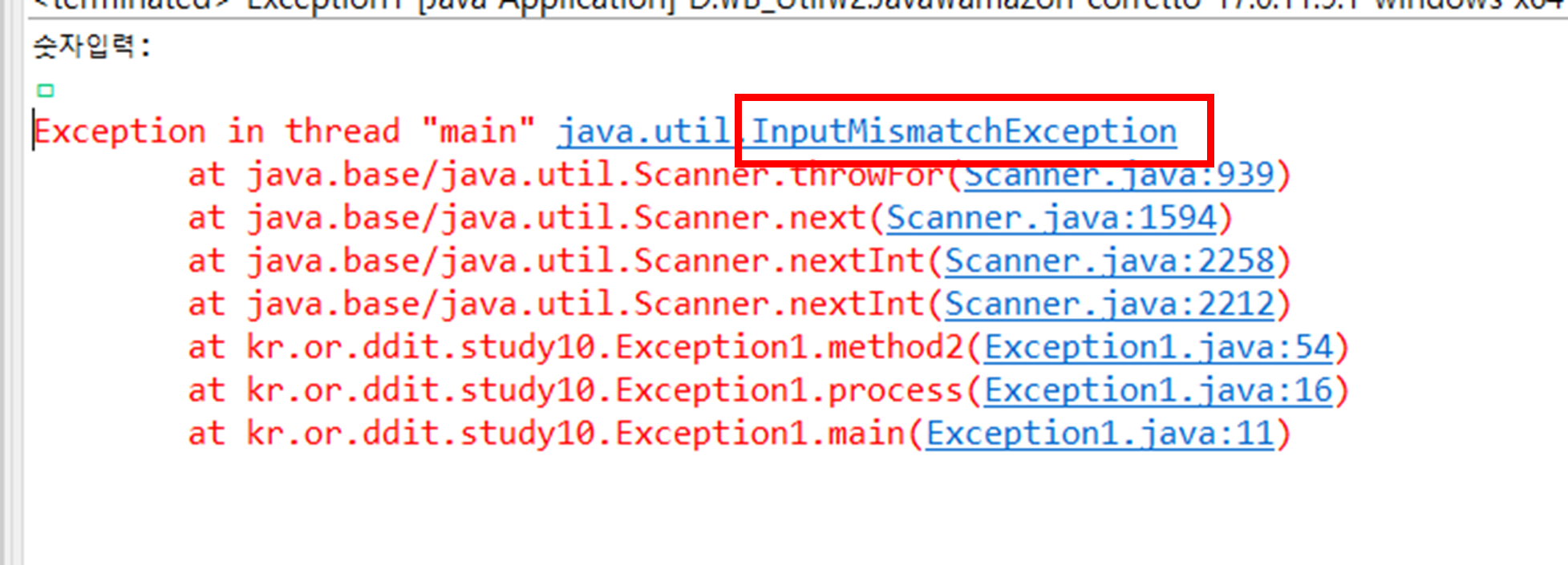
try-catch 처리하면
System.out.println("숫자입력: "); try { int num = sc.nextInt(); } catch (Exception e) { //에러 발생시 catch 구문으로 이동됨 System.out.println("숫자만 입력해주세요"); } System.out.println("정상 입력됐습니다");
이렇게 예외처리를 해줌으로써 프로그램 종료를 막을 수 있습니다.
RunTime Exception
은 컴파일 과정에서 체크하지 않기 때문에 실행시 예측할 수 없이 갑자기 발생합니다.
예를 들어 세미콜론 빼먹으면 컴파일과정에서 알수있지만,
숫자입력해야하는데 문자입력해서 생긴 에러는 실행을 해봐야 알수있는데이런 것을 Runtime Exception이라고 합니다.
public void method3() { int [] arr = new int[3]; for(int i=0;i<=arr.length;i++) { System.out.println(arr[i]); } }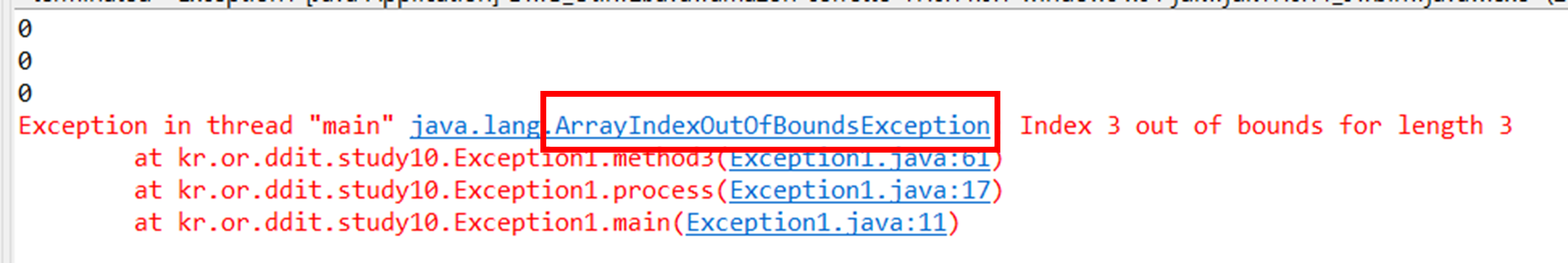
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException (index의 범위를 넘어갔다는 에러)가 난 것을 확인할 수 있습니다
for문에서 i<=arr.length를 했기 때문

에러를 처리하기 위해서는 맨 위 Exception1.java:61 을 봐야하는데
그곳을 클릭하면 실제 에러난 곳의 위치로 이동하게 됩니다.
그 부분을 try-catch로 예외처리하면
public void method3() { int [] arr = new int[3]; try { for(int i=0;i<=arr.length;i++) { System.out.println(arr[i]); } } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("배열 범위를 벗어남"); } }
프로그램이 종료되지 않습니다.
public void method1() { int[] arr = {1,2,0}; System.out.println("배열 번호 입력"); int num= sc.nextInt(); int result = 10/arr[num]; }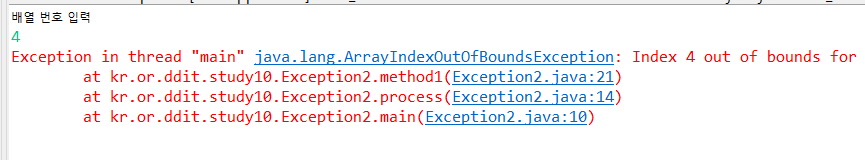
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException 에러 남
(배열범위 벗어남)

ArithmeticException 에러 남
(나누기 0)
public void method1() { int[] arr = {1,2,0}; System.out.println("배열 번호 입력"); try { int num= sc.nextInt(); int result = 10/arr[num]; } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); // 프로그램 종료 x } System.out.println("실행"); }e.printStrackTrace()를 하면 프로그램이 종료되지 않고도 에러를 출력시킬 수 있습니다.

여러 에러들을 처리하기 위해 catch구문을 여러개 할 수도 있습니다.
public void method1() { int[] arr = {1,2,0}; System.out.println("배열 번호 입력"); try { int num= sc.nextInt(); int result = 10/arr[num]; }catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) { System.out.println("배열 범위 벗어남"); } catch (ArithmeticException e) { System.out.println("0으로 나눌 수 없다."); } catch(Exception e) { System.out.println("예외 처리"); } System.out.println("실행"); }에러 이름(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException, ArithmeticException)을 catch구문에 넣어서


여러 에러를 한번에 처리할 수 있게 해줄 수 있습니다.
Throw Exception
예외 강제로 발생시키기
- 일반 메소드 내부에서 사용
- 사용 형식
throw 예외 클래스 객체명
→ IOException io = new IOException();
ex) throw new Exception();
throw IOException();왜 throw사용?
해당 메소드에서 에러를 처리할 수 없으면
강제로 에러를 발생시키고 위로 보내버립니다.
그럼 에러를 받은 쪽에서 try-catch로 에러를 처리해줘야합니다.
try { Thread.sleep(10); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }일반 예외 (컴파일 체크 예외)
Try-catch하라고 빨간줄 뜸
RuntimeException과 달리 일반예외는 자바 소스 컴파일 과정에서 해당 예외 처리가 있는지 검사합니다.일반예외는 exception을 상속받지만 runtimeException을 상속받지 않습니다.
public class Exception4 { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); public static void main(String[] args) { Exception4 obj = new Exception4(); obj.process(); } public void process() { getNum(); } public int getNum() throws Exception { System.out.println("입력: "); int num=sc.nextInt(); if(num<0) { throw new Exception(); } return num; } }
위는 메소드에서 에러 처리를 해주지 않고 그냥 넘겨버려서 빨간줄이 뜨는 겁니다.
따라서 에러를 받은 process에서
try-catch 처리를 해야 정상적으로 실행됩니다.
public class Exception4 { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); public static void main(String[] args) { Exception4 obj = new Exception4(); obj.process(); } public void process() { while(true) { try { getNum(); } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("0보다 큰 수 입력"); } } } public int getNum() throws Exception { System.out.println("입력: "); int num=sc.nextInt(); if(num<0) { throw new Exception(); } return num; } }
에러 처리를 하는 또다른 방법에는
우리가 Exception을 직접 만들어서 날리는 방법이 있습니다.
import java.util.Scanner; public class Exception5 { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); public static void main(String[] args) { Exception5 obj = new Exception5(); obj.process(); } public void process() { while(true) { System.out.println("닉네임을 입력하세요"); try { String nick = inputNick(); break; } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println(e.getMessage()); } } } public String inputNick() { String result = sc.nextLine(); if(result.length()<2 || result.length() >5) { throw new NickNameLengthException(); } if(result.contains("바보")) { throw new NickNameException(); } return result; } } //runtimeexception 상속받기 //실행했을 때 체크하겠다 class NickNameException extends RuntimeException{ public NickNameException() { super("부적절한 닉네임"); } } class NickNameLengthException extends RuntimeException{ public NickNameLengthException() { super("닉네임 길이가 2~5글자"); } }
 728x90
728x90'자바' 카테고리의 다른 글
hash (0) 2024.07.26 date, calendar (0) 2024.07.25 간단한 게시판 예제 (1) 2024.07.24 인터페이스 (2) 2024.07.24 추상 클래스 (0) 2024.07.23 다음글이전글이전 글이 없습니다.댓글